When introducing a new product to your skincare routine, I always advise patch testing first, especially if you have sensitive skin. A patch test is a straightforward diagnostic technique that determines if your skin is compatible with a new product. If inflammation, irritation, or an allergic reaction ensues, this is what we call contact dermatitis and spot testing is an easy way to suss out the cause.
The two types of contact dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when your skin comes in contact with an allergen. This catalyzes inflammation and irritation (like a rash) as an immune response. These reactions usually appear within a few days of exposure.
Irritant contact dermatitis is a non-allergic response and occurs when a chemical or physical irritant damages your skin’s outer layer. Initial symptoms are a burning or stinging sensation that manifests into prolonged itchiness and inflammation. Unlike ACD, which takes several days to appear, ICD typically flares up within several hours.
How to perform a patch test
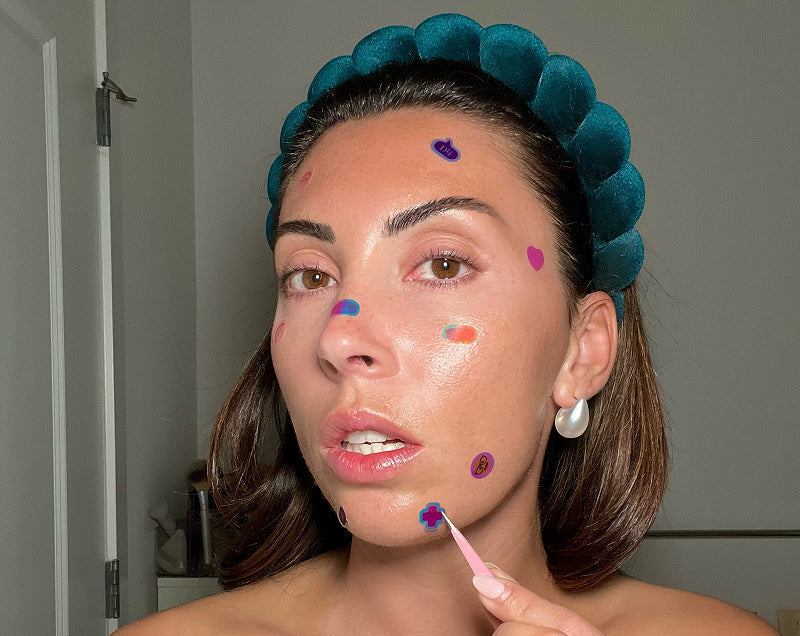
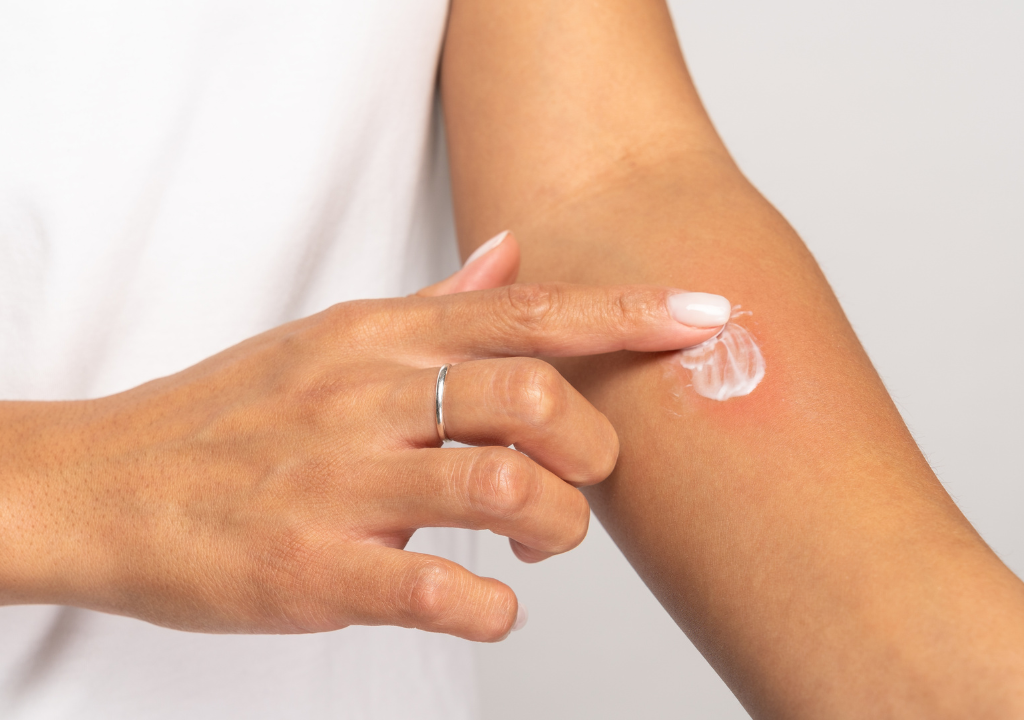
Apply a small amount of product to a small and clear patch of skin. You want to choose a "hidden" area where you won’t mistakenly wash or rub the product away. Some good spots are under your jaw, behind your ear, on the side of your neck, inside your arm, or on your elbow.
Side note: For a more accurate test, always wash and clean the area before applying the product and ensure that you haven’t applied anything else beneath.
After a minimum of 24 hours, observe your skin for any redness, itchiness, burning, and other irritations. If there are none, the product is suitable for use. But if, at any point, your skin feels as if it’s reacting, wash the product off IMMEDIATELY.